Geothermal Energy needs an idle resource that holds the potential to meet the electricity and heating demands for the future. Being a renewable and sustainable resource, the harm done to the environment is gradually low. It is carbon-free and provides a perpetual supply of heat. This energy is the affordable solution to reducing dependency on fossils-fuels and global warming.
What is Geothermal Energy?
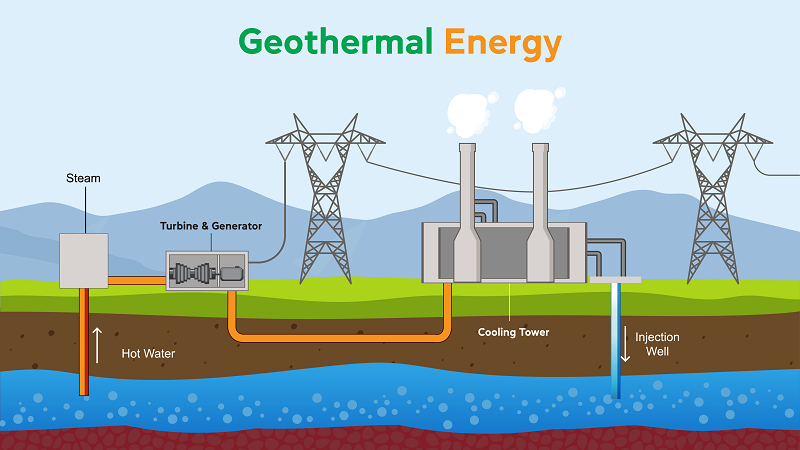
Geothermal comes from the Greek word, where ‘Geo’ refers to Earth, and ‘Therme’ refers to Heat. The heat procures from beneath the earth’s crust. Generally, it is found distantly far below the earth’s burning molten rock ‘Magma’ and stored in the rocks and vapour in the earth's centre. In the process of producing power from this energy, wells need to be dug 1.6 miles or more deep into an underground reservoir to obtain the steam and hot water there, which can then be utilized to drive turbines connected to electricity generators.
In-dept, the US Energy Information Administration writes that the planet has four parts of the layer.
i) An inner core of solid iron is about 1,500 miles in diameter
ii) Magma is about 1,500 miles thick
iii) A magma and rock locating in-depth is almost 1,800 miles thick
iv) A crust of rock that forms continents is 15 to 35 miles thick under the continents and 3 to 5 miles thick under the ocean floors
Likewise, scientists have identified that the earth’s internal central depth is about 10,800° F. The Mantle of magma ranges the temperature from around 392° to approximately 7230° F. The earth's crust fragments into parts called tectonic plates. Magma comes close to the boundaries of these plates, which is where many volcanoes happen. The lava that erupts from volcanoes is noticeably magma. Magma has numerous heat underground by which the Water and rocks absorb heat. Hence, that heat is called geothermal energy.
Moreover, Italian scientist Piero Ginori Conti invented a geothermal electric power plant in 1904, and by now, over 20 countries have produced this energy. People have been using energy for the culture of bathing in mineral springs, cooking, and eating since the millennium. Also, most Icelanders use this energy to heat their building and water. According to the International Renewable Energy Agency (IRENA), this energy had grown steadily from around 10 GW worldwide in 2010 to 13.3 GW in 2018.
Renewable energy is most likely never to end. Relatively, the underground steam and hot water produced by the decay of radioactive elements within the Earth is a natural resource generated for an unlimited time. Furthermore, a recent survey shows that almost 10% of today’s energy needs can be supported once the storage process is constructed successfully. Hence, this energy is a renewable resource.
Where does Geothermal Energy Work best?
Preferably, the suitable place that this energy works best is where extensive heat is produced. The “Ring of Fire” is an area in the nearby Pacific Ocean that has more Volcanoes than other usual regions on the Earth. Also believed that it experiences regular earthquakes and the frequent eruption of volcanoes. About 90% of the earthquake occurs, and 75% of volcanoes are located at Ring of Fire. Its length is approximately 40,000 kilometres (24,900 meters).
Repeating, Geothermal powers come from the slow decay of radioactive minerals such as Uranium, which causes the rock to become magma. Tectonic plate movement causes the movement of magma up the edges, forming a reservoir in which geothermal steam and hot water can be recovered through wells. These forms of steam or hot water are pressured through a turbine connected to a generator that produces electricity.
Specifically, the US is the leading producer of this energy worldwide, with a 3,676 MW of energy and an additional 23 MW to be added soon. Most geothermal plants are located in Western states and Hawaii because the resource is close to the earth’s surface. Then comes the top 2 Asian countries securing Indonesia's largest producing energy source with 185 MW added on existing 2,133 MW and the Philippines of 1.918 MW. Also, Indonesia owns 4 out of the world’s top 10 geothermal power projects.
Similarly, Turney appears in 4th position with 1,526 MW. The country’s biggest Power plant project is the Kizildere Geothermal Power Plant, with an installed capacity of 95 MW. In New Zealand, 13% of overall electricity is supplied using this energy. The energy is mainly generated from Taupo Volcanic Zone, and the country has an installed capacity of 1,005 MW. The South American nation, Mexico, has a capacity of 962.7 MW of energy. However, Italy introduced the energy initially, but it lands in the 7th position under the top 10 Geothermal Countries. This is because of the political climate, so it has 944 MW of power.
Next comes the world’s leading country for Safari destination- Kenya. The country is extending its 861 MW with the addition of 193.3 MW power. Next, Iceland obtains 755 MW of power, and it is famous for heating the building and water through energy. Lastly, Japan has a total of 601 MW. Also, Japan has a huge potential for this energy after the Fukushima Nuclear Power Accident. Tsunami and Earthquakes caused the disaster that happened in 2011.
Uses of Geothermal Energy
Direct use of Geothermal Heat
This is an easy alternative to access hot water, but it applies to the areas where hot springs and underground reservoirs are nearest. A production facility, a downhole, and circulation pumps or wells are used to bring up the water. A downhole consists of two types that are lineshaft pump systems and submersible pumps. Just as both types have been in practice for a long time, the lineshaft pumping system is preferred over the submersible pumps. This is because it is affordable, and submersible pumps require 800 feet of dept for the setting.
Furthermore, A mechanical facility with the transmission pipeline, heat exchanger, and the cooling system directs the necessary heat to its intended use. The transmission pipeline can either be a single pipe or a two-pipe system. The single pipe is a once-through system where the vapour is disposed of after use. This is generally preferred when geothermal energy is overflowing and when the water is pure or clean. And the two-pipe system recirculates the vapour where the residual heat is conserved.
The heat exchangers used in the geothermal systems are the plate with a mechanical seal held in a frame by clamping rods, shell and tube, and downhole types. Yet, cooling is gained by using lithium bromide and ammonia absorption refrigeration systems. Afterwards, The cooled water is stored in ponds through a disposal system.
Geothermal Heat Pump
According to the Environmental Department of Canon Global, two different wells are dug for this energy storage system. One of the underground wells is for cold water whereas another one is for warm water. Although different wells are dug, both of them are connected to an aquifer. So when the building is cooled from the cold aquifer in summer and winter, the heat is transferred through the hot aquifer.
The aquifer is operated differently. The heat present in the building will be transferred to the water. Thus, the pond store the warm water formed by the transferred heat. In winter, that warm water will heat the building because the warm water beneath will produce the heat.
Geothermal Power Plants
A Power plant either be fueled by coal, gas, nuclear power, or this energy, all of these features produce electricity through heat or steam. The Geothermal Power Plant uses hydrothermal resources like turbines, generators, transformers, and other standard power generating power to turn heat into electricity. It required an exclusively high temperature of at least 300°F to 700°F coming from dry steam wells or hot water wells. Further, the wells are dug 1-2 miles deep into the surface, and then people use the piping the steam or hot water technique. This powers a turbine that generates electricity. Again such power plants are usually found nearby hot springs, geysers, and volcanic erupted areas.
First, the hot water is pumped from the deep underground through a well with high pressure. After the water reaches the surface, the pressure is dropped. The pressured water will be warmer, which allows the water to turn into steam. The turbine is spun by steam. It is connected to a generator. Overall, the generator assists in producing electricity by sending an electrical current to a step-up transformer outside the power plant. Voltage is increased in the transformer, and the current is transmitted over the power lines to buildings. Further, the steam cools off in a cooling tower and consolidates back to the water. The chilled water is withdrawn again into the Earth to start the process again.
In contrast, the World's largest geothermal plant is the Geysers Geothermal Complex of the US. It has a total capacity of 1,517 MW. It is made up of 22 power plants and spread over several kilometres North of San Francisco. It lies on the tip of deep magma that stretches over 30 square miles. Likewise, the second largest is taken with Larderello Geothermal Complex, Italy. It comprises 34 plants with a total net capacity of 769 MW. Then Cerro Prieto Geothermal Power Station of Mexico features 4 plants and has 720 MW energy remarks as the third largest power plant globally.
Types of Geothermal Power Plant
Dry Steam Power Plant
There are three main types of Geothermal Power Plants: Dry Steam Plants, Flash Cycle Steam Plants, and Binary Cycle Plants. The Dry Steam Plants use steam naturally produced from the ground. The steam comes from the production of the well to turn the generator turbines. This is only possible at the places having the highest temperatures. The temperature varies from 212°F to 608°F. However, it requires less vapour, but the extracted water will be in the form of gas. Italy constructed the first geothermal power generation plant from a dry steam power plant in 1904. This had the power of 250 Kilowatt.
Flash Steam Power Plant
In the same way, Flash Cycle Steam Plants doesn’t use steam directly from the earth to generate electricity. Rather it pumps hot water at high pressure below the earth. This is done through the well into the flash tank that is kept at a lower pressure. Due to the flash tank’s low pressure, the hot pressure turns into steam. Then the steam will spin the turbines and generate electricity. Here the water must be over 356°F. This is the widely practised type of plant in the present context. In the end, the cooled water returns to the underground water tank to be heated by geothermal rocks again.
Binary Cycle Power Plant
The last is Binary Cycle Plants, which transfers the heat from geothermal hot water to another liquid. The heat causes the second liquid to turn into steam which helps to drive the turbine generator. This is likely to be considered as the commonly used energy in the future. Also, it works under lower temperatures (224.6°F to 359.6°F), but the other two types can’t. Binary Cycle Plants use the heat from underground reservoirs to heat the second vapour with a low boiling point instead of using the water and steam directly. Then it spins a turbine and generates electricity. It has a thermal efficiency of 10-13%.
Types of Geothermal Energy Systems
This energy system is an alternative to that source using high electrical energies. This system is efficient, environmentally friendly, easy to use, and affordable. It uses almost half less energy than other conventional heating or cooling systems. Though there are several options to choose from in these energy systems, the environmental needs and demands should be strictly observed. Firstly the types of geothermal energy systems are:
Closed Geothermal Loop System
The closed geothermal loop system is high energy efficient that distributes heat equally in the house by reducing the reliance on fossil fuels. The installation cost could be expensive, but it can last up to 25 years+. Despite that, it absorbs the natural heat from the ground itself and then releases it equally to the particular house. The system combines a heat pump that draws water and antifreeze solution through an underground water pipe buried at shallow depths in your yard. As it requires little maintenance, it provides warmth in a renewable way.
- Horizontal Ground Source of Heat Pump
It requires larger space as two pipes need to be buried parallelly in a maximum of 2 meters down the horizontal trenches. The advantage of this type of Earth loop installation is that more pipe per meter is used in a smaller trench area, making it a more compact design for smaller gardens or plots. However, the disadvantage is that the heat resource can be easily removed from a much smaller footprint. This results in less heat extraction from the ground.
- Vertical Ground Source of Heat Pump
Identically, a vertical ground source of heat pumps is costlier than the horizontal ones, but it can also be installed in a restricted area. And this option doesn’t need larger pipes because the requirement of a drilling rig to drill boreholes is about 80 meters deep. The disadvantage of a vertical ground source heat pump is that depending on the water being used from the well, water filters and periodic cleaning of the heat exchanger might be necessary inside.
Open Geothermal Loop System
The Open Geothermal Loop system works by pumping the groundwater from an aquifer or similar and carrying it to the heat pump. That means the evaporator transfers its heat. After that, the water is either re-injected into the ground or discharged to the surface. Thus, the heat source is similar to the fluid that runs by the circuit, and it has to be replaced persistently because it is not re-circulated. The advantage of the system is that it is comparatively affordable than the other system.
- Closed Loop System for Pond/Lake
This type is possible where there is an adequate amount, and deep water is present. A pipe is settled underground from the location to the pond/lake so that the freezing winter doesn’t bother all. While it is more expensive to install than the open-loop system, it eliminates the continuous intake of well water. As in the case of any closed-loop system, there are no harmful effects on the environment.
Advantage of Geothermal Energy
The advantages of using this energy are as follows:
a) Reliable
Unlike solar and wind energy, this energy doesn’t fluctuate. The energy is always available, so there is no requirement to depend on other factors to generate the power. So the calculation process is simple, which makes it easy to predict the energy outcome.
b) Environmental friendly
Though this energy is withdrawn from beneath the earth, the fields produce no emissions. The carbon footprint of the geothermal power plant is minimal, on which it releases 99% less carbon dioxide for every megawatt-hour of electricity it generates. There might be other polluting aspects, but that seems to be less than other resources produce. For example, free hot water and electricity production doesn’t cause noise pollution.
c) Massive potential holder
According to data by Learn Mechanical, The power plants distribute 12.7 GW of electricity while every other resource delivers 17 Terawatts worldwide. In insomuch, it is estimated that geothermal power plants have the potential of 0.035 to 2 TW. After that, geothermal heat pump systems use 25% to 50% less electricity than conventional systems for heating or cooling, requiring less space for types, and it is inexpensive. Considering that there is a huge potential for this energy generation.
d) Great for heating and cooling
Energy plays a significant role in heating and cooling. Icelanders have been using this facility for a long time back. This doesn’t require a higher temperature, but the steam between the surface and a well-dug of just 2 meters can be enough. This will help in heating and cooling the building or houses, which increases the homeowner’s savings.
e) Renewable and sustainable
This is the natural resource that will be accessible till the planet is eradicated. Plus, it is independent while comparing to other resources. According to scientists, geothermal reservoirs are expected to last for billions of years. Fossil fuels are meant to have an expiry date, but geothermal energy has no limitation of ending. This makes the power both renewable and sustainable.
f) Rapid Evolution
This era has introduced unexpected technologies to improve every dimension of each field. Similarly, technologies for exploiting natural resources have been created too. It shows that the trend of growth in this field is increasing. Hence, Indonesia and the Philippines are constructing a massively huge power plant for a better future.
Disadvantages of Geothermal Energy
Nevertheless, every part belonging to the universe has both pros and cons. Likewise, this energy is a definite environmentally friendly resource, but some aspects harm our surroundings. To know more about the disadvantages, the following points have been explained thoroughly.
a) Environmental Issues
According to the Union of Concerned Scientists, there are plenty of greenhouse gases located underneath the earth. Some greenhouse gases escape towards the ground and into the atmosphere whenever this energy is used. Besides, the emissions tend to be higher while comparing to geothermal power plants. It is because the power plants generate a lesser amount of sulfur dioxide and silica emissions.
Sometimes the reservoirs are detected with toxic heavy metals, including mercury, arsenic, and boron. The pollution associated with geothermal power is very low and just a tiny fraction of what we see with coal power and fossil fuels. Furthermore, there have been no reported cases of water contamination from geothermal sites in the US.
b) Higher initial cost
Though the energy provides free heat production, the initial capital costs tend to be higher. This is because the cost of drilling wells for the underground waterbody is expensive. Besides, installing the heating and cooling system is necessary, which is way more costly than drilling the wells. The reason for the expensiveness is the advancement of the installation of technologies. For instance, an installation of a general heating pump might cost about $10,000-$20,000. The Return On Investment is predictable for sure, but it will consume a long time.
c) Preferable in certain areas
This energy is specifically extremely hot under surface areas. Nonetheless, the hot rock should be suitable enough to dig the wells. Every type of rock won’t help in digging the well, whereas the hot bearing capacity differs from one another. Generally, such places are located away from the city where there is less population. Or it can be observed as the most volcanic erupted places are suitable for the huge production of energy.
People normally neglect frequent natural calamities occurring in places. Thus, overproduction could harm the environmental issues because the necessity is at a populated place.
d) Cause surface instability
When a surface is drilled, there is a possibility of causing the surface to be unstable and trigger an earthquake. The traditional geothermal power plant construction requires drilling hot rock. Those contain trapped water or steam in their opening spaces and natural explosion. When these splits are divided by a drilled hole, the trapped water explodes as steam.
The drilling itself may not trigger earthquakes, but the rupturing of steam and subsequent return of the used water to the hot water reservoir could. The cycle leads to uncertainty along bursting lines that might result in an earthquake.
e) Experience dry spell
Geothermal heat approaching from the waterbody beneath may die down or run out of steam even after years of usage. The scarcity of every aspect needed for land may last decades, which is why it’s recommended to use the heat prudently and not abuse it. Incompatible use can also result in an impoverished distribution of heat.
Conclusion
The practice of this energy has existed for ages, rapidly increasing over the last three decades, for both uses of generating electricity and direct use of heat. At the outset, the efficiency of a geothermal system is only 20%, but that is common among power generation facilities. The environmental impacts of the energy facilities are less than any other natural resource. It produces no emissions with 99% less carbon dioxide to mass-produce electricity.
For instance, Wells of at least a mile deep or more are drilled into underground reservoirs to connect with the geothermal resources. These resources can be exploited from naturally occurring heat, rock, and water or through enhanced geothermal systems, which enhance or create geothermal resources through hydraulic stimulation. These geothermal resources, whether natural or enhanced, drive turbines linked to electricity generators and produce heat.
In winter, a geothermal heating pump system can upgrade the temperature of the upper 3 meters of the Earth’s land. This happens when the heat is extracted from the houses and transferred to the cooler ground in the summer. Geothermal water from deeper into the Earth can be used directly to heat homes and offices or grow plants in greenhouses. Some U.S. cities usually place the geothermal hot water energy’s pipe under roads and sidewalks to melt snow.
Exponentially, this energy is taken as being too practical from an economic viewpoint. It is considered a cheap, never-ending resource and a base-load generator. However, the geothermal power plant isn’t cheap to install. It requires advanced technologies and human resources before the heavy Return on Investments. Well, the first country to use the prospects of Geothermal energy was Italy in 1904. Similarly, it is believed that the monkeys of Japan used this method from hot springs. The motive was to keep itself warm during winter. Today, the United States is the largest producer owning the World’s largest geothermal development is located at the Geysers North of San Francisco, California.
We hope you have enjoyed our content on Geothermal Energy. Do you think we missed something? Do you know of some other way this energy contributes worldwide? Feel free to comment below. We always appreciate your suggestions.

 How it Works
How it Works Pricing
Pricing FAQ
FAQ Quiz
Quiz Contact Us
Contact Us